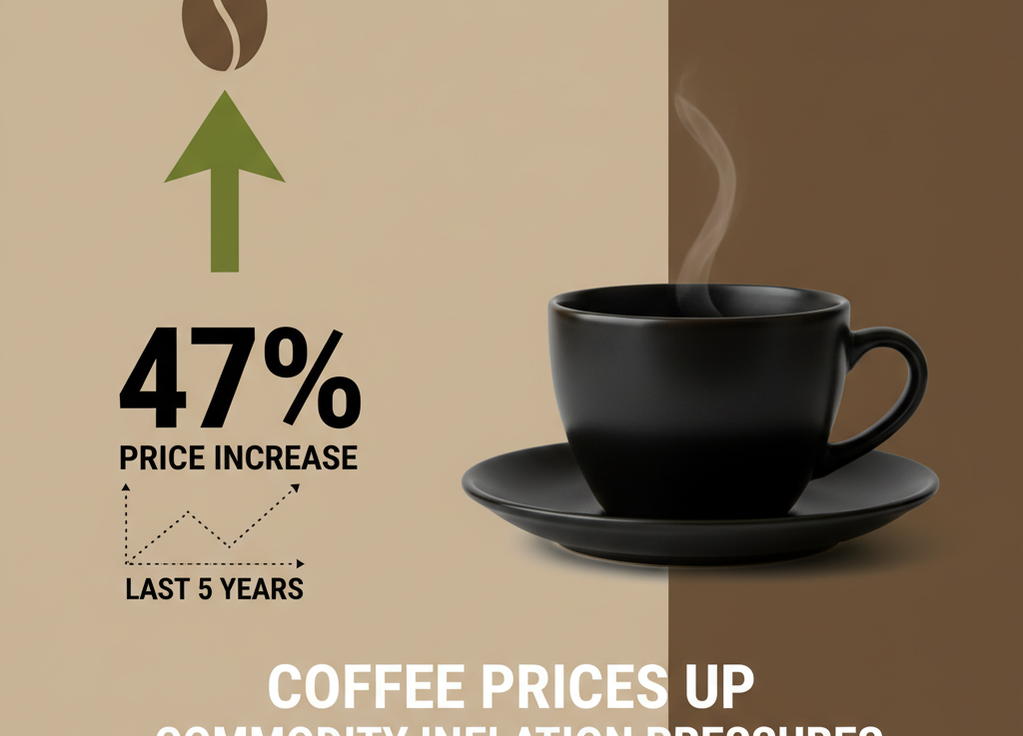
Coffee Prices Up 47% in Five Years: Commodity Inflation Pressures
Sarah Lee
February 16, 2026
Coffee Prices Up 47% in Five Years: Commodity Inflation Pressures
The aroma of freshly brewed coffee has become an indispensable part of daily life for many. But for those who pay attention to the numbers, the reality is sobering: coffee prices have surged by 47% over the past five years. This steep increase is emblematic of broader commodity inflation pressures affecting consumers and businesses alike.
Key Takeaways
- Coffee prices have risen 47% over the past five years due to various economic factors.
- Specialty coffee shops have contributed to increased demand, elevating consumer expectations and prices.
- Supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by climate change, have affected coffee production globally.
- Economic conditions, such as inflation and geopolitical tensions, further strain coffee supplies.
- Consumers may need to adjust their coffee budgets or seek alternatives as prices continue to rise.
The Specialty Coffee Boom
In the early 21st century, the rise of specialty coffee shops transformed coffee from a simple morning ritual into a cultural phenomenon. Chains like Starbucks and local artisanal cafes have set high standards for quality, driving a demand for premium beans. This trend has not only elevated consumer expectations but also pushed prices upward. When customers are willing to pay more for a superior product, suppliers respond accordingly, and that’s where we see the beginnings of price inflation.
Notably, younger consumers, particularly Gen Z, are gravitating toward specialty coffee experiences. This demographic's willingness to invest in high-quality brews has become a significant factor in driving market prices higher. For coffee businesses, this is both an opportunity and a challenge, as they must balance quality with affordability.
Supply Chain Challenges
While demand is a critical driver, supply chain issues have compounded the situation. Climate change has severely impacted coffee-growing regions, particularly in South America, where unpredictable weather patterns have led to fluctuating harvests. Droughts, excessive rainfall, and pests have all played a role in diminishing yields. As global temperatures rise, the areas suitable for coffee cultivation may shrink, further tightening supply.
Additionally, logistical disruptions stemming from the COVID-19 pandemic have made it harder for coffee to reach consumers. Shipping delays, increased freight costs, and labor shortages have all contributed to rising prices. As suppliers face these challenges, the costs are inevitably passed down to consumers.
Economic Pressures
The current economic landscape is another layer of complexity. Inflation rates have surged globally, impacting everything from groceries to gasoline. Coffee, being a commodity, is not immune to these pressures. As production costs—such as labor, fertilizers, and transportation—rise, so do the prices at the cafe.
Geopolitical tensions, such as those arising from conflicts in major coffee-producing countries, also exacerbate the situation. Supply constraints from these regions can lead to market volatility, making it difficult for consumers to predict coffee prices. The cumulative effect of these factors has made coffee a luxury that some consumers may need to reconsider.
Consumer Impact and Future Outlook
As coffee prices continue to rise, consumers are starting to feel the pinch. Many are adjusting their coffee habits, whether by brewing at home or opting for less expensive brands. The specialty coffee craze may face a reckoning if prices keep climbing.
For businesses, this can be a double-edged sword. Higher prices may boost profit margins, but they also risk alienating price-sensitive customers. Therefore, cafes and roasters must navigate this tricky terrain carefully. Strategies like offering loyalty programs, diversifying product lines, or even focusing on sustainability could help mitigate the impact of rising costs.
Looking ahead, it’s unclear whether coffee prices will stabilize or continue to climb. Climate change, ongoing supply chain issues, and consumer behavior will all play pivotal roles. What is certain is that coffee lovers need to be prepared for a changing landscape.
Conclusion
Coffee has woven itself into the fabric of modern life, but the rising prices are a wake-up call. As consumers, businesses, and producers navigate these inflationary pressures, it's crucial to remain adaptable. Whether it’s experimenting with new brewing methods or seeking out alternative beverages, the art of coffee appreciation may require a fresh perspective. In a world where change is the only constant, perhaps the love for coffee can survive the storm—if we’re willing to rethink how we engage with it.